Walkable ground learning and estimation
Contents:
Author
- Jose Pardeiro
- Score: 10/10
- Sept. 10th 2013: An extension of this work has been accepted in the 1st Iberian Robotics Conference ROBOT2013.
Objective
The objective is to implement and adapt an algorithm which is able to detect the walkable ground next to the robot. From its colour characteristics, models of ground are learnt. Later, with an RGB camera the environment of the robot is analyzed in order to estimate ground with the same color characteristics.
The results are that we are able to estimate walkable ground in places which are farther away from the Kinect that its depth range (approximately 6-7 meters). Moreover, we have tested the algorithm in shiny grounds, reducing the depth range to 2 metres (because the rest of the range was lost due to reflections).
Results pictures shows the original RGB image, the walkable ground detected using depth information from the Kinect, and the final result of the algorithm, estimating the rest of the corridor (light blue) within an area of interest automatically computed (green lines).
Results

From left to right: Initial image, floor detected with 3D data, floor detection improved with RGB data.
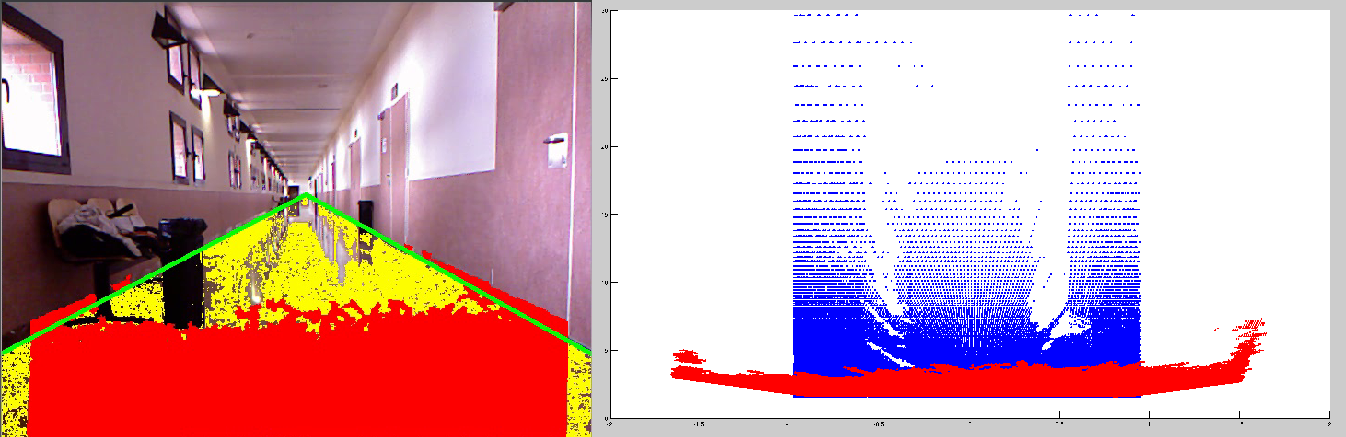
Red is real ground, obtained with the Kinect camera and the blue points are estimated ground.
Documentation and Source
- Report (spanish)
- Source code
- Paper: J. Pardeiro, J.V. Gómez, D. Álvarez and L. Moreno, Learning-based Floor Segmentation and Reconstruction, Iberian Robotics Conference (ROBOT2013). Madrid, Spain. November, 2013.